Mammals and birds represent two different groups within the animal kingdom that share some similarities while also boasting unique qualities that set them apart. A better understanding of these creatures’ adaptations and evolutionary journeys is vital in order to appreciate all they offer us as a species fully.
Are you curious to understand the differences between birds and mammals? In this article, we will outline their unique features as well as provide comprehensive details.

Difference Between Mammals and Birds
Difference Between Mammals and Birds
Mammals vs Birds
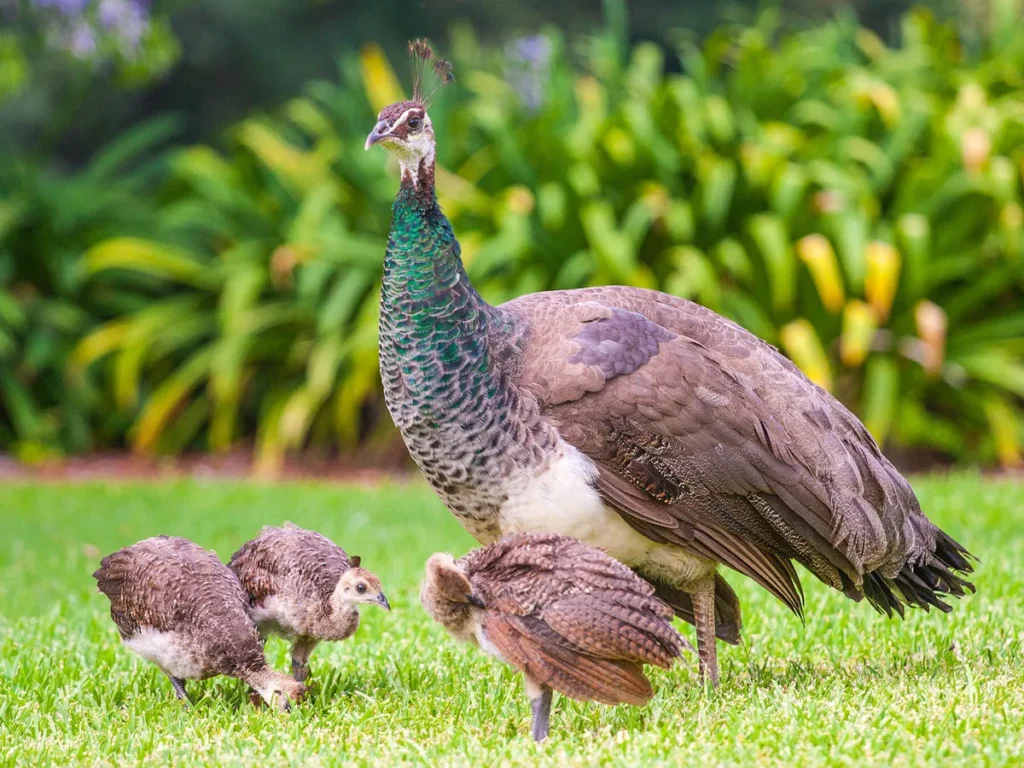
When thinking about the differentiators between birds and mammals, one of the things that occur to mind is that mammals birth their children, while bird eggs are laid by birds.
Let’s examine the other differences between birds and mammals. The birds have feathers while mammals only have hair or fur. This is one of the primary characteristics of birds that distinguish the species of mammals from birds. Birds have feathers to control body temperature, fly, and even attract the opposite sex.
Because birds fly to fly, they have porous, bone, or hollow ones. On the other hand, mammals have more dense bones. Birds are able to fly, but mammals have hands, paws, and hooves.
Additionally, there’s a distinction in the way that they feed their young. Mammals feed their babies with milk produced by glands that produce milk. However young birds are fed by their parents, who are able to regurgitate food partially digested.
Both mammals and birds have a larynx. The mammals make sounds through the larynx. In birds, the organ is not able to produce sounds. The larynx is not used to produce sounds, birds use a syrinx that functions as a vocal box.
In the lungs of bird species, they do NOT expand or contract like those of the mammals’ lungs. In mammals, carbon and oxygen dioxide are exchanged in the alveoli which are tiny sacs inside the lung. In birds, this exchange occurs within air capillaries that are the walls of microscopic tubules. There is only one breathing cycle that mammals have There are two respiratory cycles for birds.
Comparing blood samples with the blood of birds, there is an RBS nucleus however it isn’t commonly found in mammals. When there’s no nucleus inside the RBS of mammals, this is a sign of sickness. In birds, the RBS has an oval form, while the majority of mammals’ RBSs are circular shape.
Physical Attributes: Fur vs Feathers
One of the most distinguishing characteristics between animals is their fur or feathers. Mammals, from small bats to massive blue whales, all share one feature – hair or fur! Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals – even marine ones like whales and seals have it at some stage during their life cycles!
Birds, on the other hand, are covered with feathers that serve an important purpose, not just aesthetic appeal. Feathers provide insulation to keep birds warm in winter weather conditions, while waterproofing helps them avoid being submerged by water bodies or providing aerodynamic advantages during flight.
Fur and feathers both possess unique properties that serve an important function for animals possessing them, including warmth, protection, camouflage capabilities, and visual displays that attract mates or intimidate rivals.
Animals have evolved various physical attributes in order to thrive within their environments and fulfill their ecological roles. From fur to feathers, animals possessing these features have thrived within their respective ecosystems and fulfilled their ecological roles accordingly.
Bearing Offspring: Live Birth vs Egg Laying
Reproduction methods differ between mammals and birds significantly. Mammals like humans, elephants, and dolphins give live birth after fertilization of an embryo within their mother’s uterus. She provides nutrients and protection until the baby is ready to leave its mother’s womb and be born into the world. In contrast, birds lay eggs to produce offspring.
Birds such as chickens, eagles, and penguins all use eggs as a form of reproduction. A female bird lays fertilized eggs containing developing embryos before incubating them until hatching occurs – providing an environment in which offspring can develop away from its mother’s body.
Understanding the differences between viviparity and oviparity sheds light on both mammals’ and birds’ reproductive strategies, as well as illuminating how new life enters this world in various forms.
Raising The Young: Parental Care
Parental care is an integral component of animal parenting. Different species display various levels and strategies of parental care to ensure the survival and well-being of their offspring, with mammals and birds known for taking different approaches when raising young. This category explores these differences.
Mammals, including humans, provide extensive parental care for their offspring. Mammal newborns depend on their mothers for survival after birth. They must rely on them for nourishment from milk produced by mammary glands – which produce the nutrient-rich substance known as mother milk to ensure their young survive and thrive during the early stages of life.
Conversely, birds also display an array of parental care behaviors. Some species leave their hatchlings to fend for themselves soon after birth; others engage in extended feeding and protection practices for an extended period after birth.
The level of parental care among birds varies significantly based on species and environmental considerations.
We delve into the fascinating world of Raising The Young: Parental Care, exploring how mammals and birds care for their young to ensure survival in nature.
Heart And Blood Circularion: Four Chambers vs Three Chambers
Comparing four-chambered hearts between different animal species provides valuable insights into how their circulatory systems operate under various environmental conditions.
While both mammals and birds possess four-chambered hearts, their structures, sizes, and functioning differ significantly, mammalian hearts tend to be relatively larger in relation to body size, while avian hearts beat faster, as this difference mirrors metabolic demands in each animal species.
Both groups employ a double circulatory system consisting of systemic circulation (body) and pulmonary circulation (lungs). However, birds boast more efficient systems due to their higher metabolic rates and increased energy expenditure, assisted by their unique three-chamber heart structure that minimizes mixing between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Overall, comparing four-chambered and three-chambered hearts illustrates the flexibility of the circulatory system in meeting the differing needs of various animal species. By understanding these variations in heart chamber arrangements, researchers can gain valuable insights into its evolution and function across a wide range of species.
Respiratory systems of birds and mammals differ
Birds rely on air sacs to ensure efficient respiration: Birds possess air sacs that ensure an uninterrupted supply of air to their lungs, increasing oxygen exchange during respiration.
Mammalian Respiratory System Adaptations: Mammals possess lungs that expand and contract to facilitate oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanges.
Comparison of Lung Structures: Comparing bird and mammal lung structures shows distinct variations in complexity and efficiency according to their breathing needs.
Mammals and birds have similar feeding habits
Mammals and birds share similar feeding habits despite differing diets. Both species engage in feeding their young in various ways; birds may regurgitate food for chicks, while mammals might nurse offspring directly.
These similarities can be traced back to a shared ancestor who laid out unique feeding strategies suited to birds’ and mammals’ lifestyles. Both groups have evolved specialized feeding adaptations, such as beaks for birds or special teeth for mammals, in order to access and consume their food sources efficiently.
Overall, these similarities between the feeding habits of mammals and birds highlight their evolutionary connections.
Similarities between mammals and birds
Exploring the similarities between mammals and birds is both fascinating and thought-provoking despite their distinct species characteristics. Both have vertebrates with backbones, sharing one characteristic: high body temperatures relative to other animals.
Mammals and birds share many similar behaviors and adaptations that enable them to adapt to diverse environments, but when it comes to reproduction and parental care, they differ significantly.
Mammals usually give birth live and nurse their newborns with milk produced by their mothers; birds, on the other hand, lay eggs that hatch and provide care to their offspring through various means.
Understanding the similarities and distinctions between mammals and birds sheds light on the complexity of nature and demonstrates its incredible diversity on Earth.
Common characteristic between mammals and birds
Birds and mammals both possess the characteristic of homeothermy or being warm-blooded, which means they can regulate their internal body temperatures to remain at an ideal level regardless of external temperatures. This allows both species to maintain constant temperatures regardless of external stimuli.
Birds and mammals differ from cold-blooded creatures like reptiles and amphibians in that their body heat is generated internally through metabolic processes rather than external sources such as sunlight.
Cold-blooded creatures like reptiles rely on external heat sources such as the sun to maintain an ideal body temperature for survival; birds and mammals, on the other hand, generate internal heat through metabolic processes.
Homeothermy provides both groups with the ability to thrive in various environments and climates, as it enables them to adjust to diverse environments and climates with ease. Furthermore, this process supplies them with energy for activities such as flight, hunting, and long-distance migrations.
What’s the difference between birds and mammals
There’s a vast array of living things on earth and among them, those from the animal kingdom are likely to be the ones that enthrall us most. Mammals and birds are both impressive, however, they differ in many ways.
In terms of numbers, it is true that only a small percentage of living creatures have skeletons, and a smaller percentage of vertebrates have the ability to regulate their body temperatures.
It is the classes, Aves, as well as Mammalia, that have the two groups that possess this particular warmth-blooded characteristic, and it frequently leads people to believe that mammals and birds are inextricably related. Sometimes, even birds are a species of mammal.
It’s true, however, that the two classes differ in a variety of ways. It’s more than just the reality that we aren’t able to fly.

Definiting the Problem
For starters, the two species differ in their definitions. A bird’s definition is one with feathers and a toothless mouth, wings (usually that allow for flight), and the capacity to lay eggs with a hard shell. In addition, mammals have hair they have live children and females generate milk from their mammary glands the structure that is the reason why the class is called.
There are some kinds of species that blur lines slightly.
Concerning the subject of wings, care must be taken not to focus too much on the flight itself, as many species of birds, such as penguins, have wings that are modified specifically designed to move through the water. Of course, there are numerous birds that are flightless.
In addition, mammals with wings that are able to fly, bats. However monotremes (a group of mammals that includes Echidna and platypus) make things more complex,
Monotremes challenge mammalian norms to adopt bird-like behaviors. Even though they’re mammals who lay eggs instead of giving birth to live babies however it needs to be said that platypus and echidna species are unusual mammals, so we shouldn’t base our conclusions on them (but that’s a discussion in a separate article).
In light of these facts that even the bat’s modified forelimb does not have feathers, and after the egg-laying process, monotreme mamas will feed their babies through a milk-based diet.
The ability to judge books based on the covers
As humans, it’s reasonable to presume that we have the basic idea of what mammals are at the very least, the basic.
However, few of us take the time to look at the distinctive shape of a bird. First of all, even though there are a lot of variations in mammalian shapes, the fundamental structure of the bird’s body is pretty uniform and usually quite different from that of a mammal.
When you consider only the typical mammal shape, which has four similar-sized limbs as well as a tail, there are significant differences in the overall structure of bird bodies.
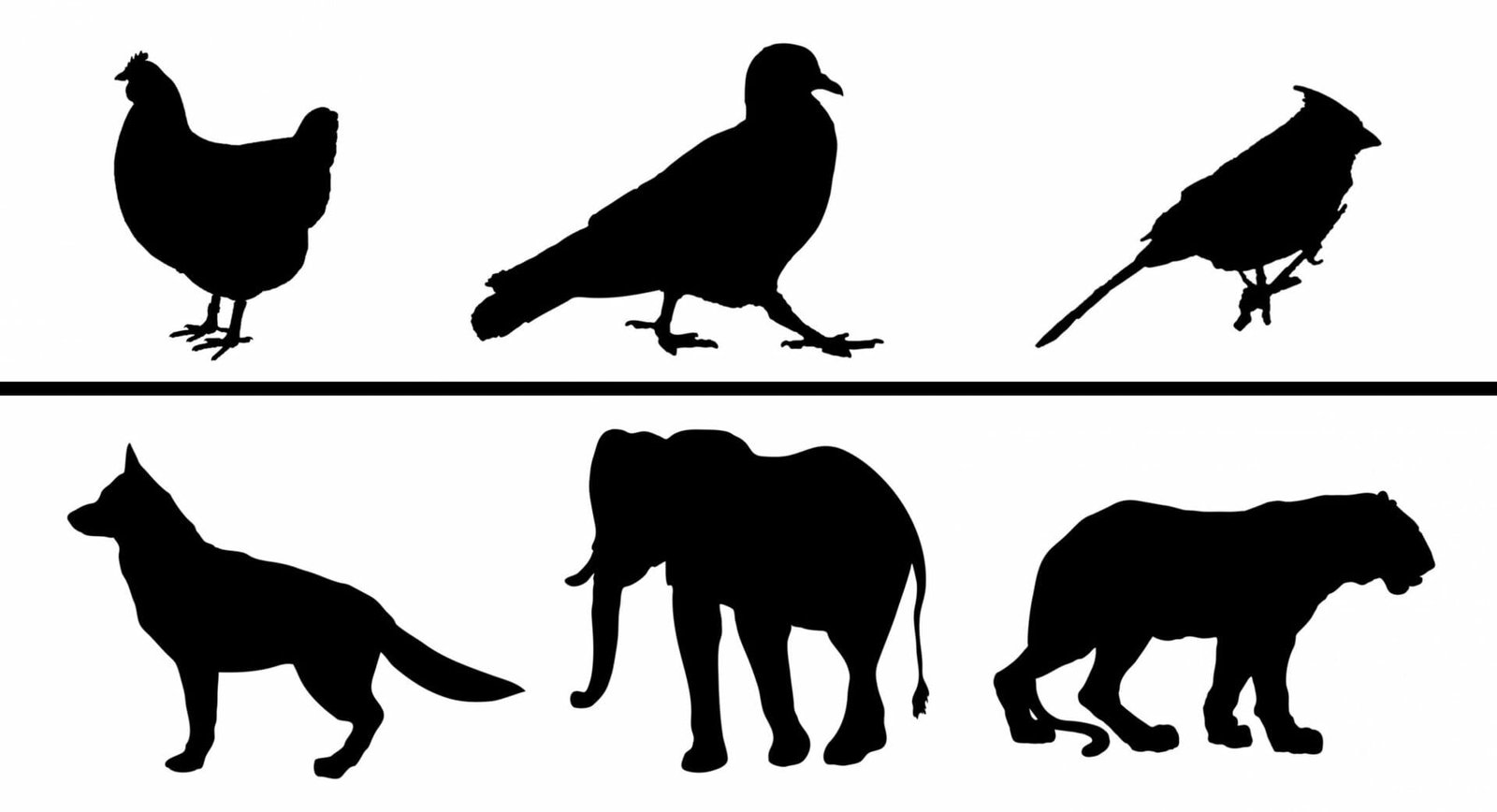
Now, let us take a closer look. If you’ve got one of your pets you can look at it with a smile and perhaps it will reciprocate with a giddy gaze.
There are mammals that have teeth, while the bird’s smile can be equally sharp, however, it’s not in a position to return the gleeful smile because, as opposed to mammals, the birds do not have teeth. The next thing to be aware of is perhaps the most obvious: the lovely, slightly rounded feathery bodies.
Unlike mammals, where mammals have forelimbs, birds wear wings. However, even though they do not have hands to hold objects, if you look at them from a lower angle, they’re sporting gorgeous wrinkled clawed feet.
Birds generally have four toes with three of them facing forward and one backward. This is the part that we normally consider as feet of birds. But, they are usually digital, meaning they walk with their feet. What we consider to be their knees actually are their ankles.
The felines and canines are digitigrade, but of course, the feet appear different. That’s just an outside view. Let us get even closer.
FAQS
What are the main characteristics of mammals?
Warm-blooded nature of mammals: One of the primary characteristics of mammals is their warm-bloodedness, enabling them to regulate their body temperatures internally.
Mammary Gland in Mammals: Mammals have mammary glands to produce milk to feed their young.
Mammals give birth live: As opposed to birds and most reptiles, mammals give birth live rather than laying eggs.
How do birds differ from mammals?
Feather Structure in Birds: Birds are distinguished by their distinct feather structure, which allows for flight while providing insulation.Birds’ respiratory systems feature air sacs for efficient oxygen exchange.
Birds Lay Eggs: Birds reproduce by laying eggs that they incubate until hatching, unlike mammals, which reproduce via reproduction through gestation and birthing of embryos.
What are the similarities between birds and mammals?
Birds and mammals both belong to the vertebrate kingdom, each possessing both a backbone and an internal skeleton.
Similarities between birds and mammals in their warmth: Both birds and mammals are warm-blooded creatures, maintaining an even body temperature throughout.
Reproductive methods in birds and mammals: Both groups demonstrate complex reproductive behaviors; birds lay eggs while mammals give live birth.
Can birds and mammals have similar feeding habits?
Comparing Feeding Strategies of Birds and Mammals: Birds and mammals alike have developed different feeding strategies adapted to their dietary requirements and ecological niches.
Diet variations among bird species: Different bird species display distinct diets, from nectar-feeding to carnivorous behaviors.
Digestive systems of mammals and birds: Both mammals and birds possess distinctive digestive systems that process their respective diets efficiently.
Summary:
- Mammals birth their children, while the birds lay eggs.
- They have feathers, whereas mammals have hair, fur, or fur.
- Birds have hollow or porous bones. However, mammals have more dense bones.
- The birds have wings, and mammals have paws, hooves, and hands.
- Animals produce sounds using larynxes, however in birds, the organ is not able to produce sounds. Instead, the birds have the syrinx, which acts as an instrument for speaking.
- Mammals feed their babies with milk produced by mammary glands. In contrast, babies are fed from their mothers, who re-inject foods that are partially digested..






